EIP-6059: Parent-Governed Nestable Non-Fungible Tokens
An interface for Nestable Non-Fungible Tokens with emphasis on parent token's control over the relationship.
| 作者 | Bruno Škvorc, Cicada, Steven Pineda, Stevan Bogosavljevic, Jan Turk |
|---|---|
| 讨论-To | https://ethereum-magicians.org/t/eip-6059-parent-governed-nestable-non-fungible-tokens/11914 |
| 状态 | Draft |
| 类型 | Standards Track |
| 分类 | ERC |
| 创建日期 | 2022-11-15 |
| 依赖 | 165, 721 |
| 英文版 | https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-6059 |
目录
摘要
The Parent-Governed Nestable NFT standard extends EIP-721 by allowing for a new inter-NFT relationship and interaction.
At its core, the idea behind the proposal is simple: the owner of an NFT does not have to be an Externally Owned Account (EOA) or a smart contract, it can also be an NFT.
The process of nesting an NFT into another is functionally identical to sending it to another user. The process of sending a token out of another one involves issuing a transaction from the account owning the parent token.
An NFT can be owned by a single other NFT, but can in turn have a number of NFTs that it owns. This proposal establishes the framework for the parent-child relationships of NFTs. A parent token is the one that owns another token. A child token is a token that is owned by another token. A token can be both a parent and child at the same time. Child tokens of a given token can be fully managed by the parent token’s owner, but can be proposed by anyone.
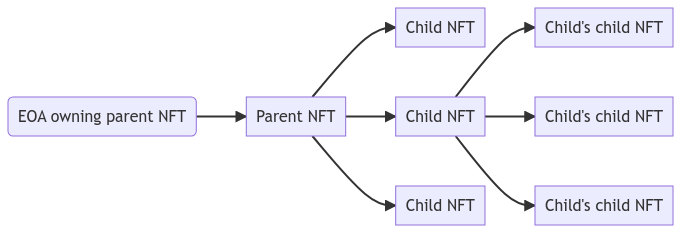
The graph illustrates how a child token can also be a parent token, but both are still administered by the root parent token’s owner.
动机
With NFTs being a widespread form of tokens in the Ethereum ecosystem and being used for a variety of use cases, it is time to standardize additional utility for them. Having the ability for tokens to own other tokens allows for greater utility, usability and forward compatibility.
In the four years since EIP-721 was published, the need for additional functionality has resulted in countless extensions. This EIP improves upon EIP-721 in the following areas:
Bundling
One of the most frequent uses of EIP-721 is to disseminate the multimedia content that is tied to the tokens. In the event that someone wants to offer a bundle of NFTs from various collections, there is currently no easy way of bundling all of these together and handle their sale as a single transaction. This proposal introduces a standardized way of doing so. Nesting all of the tokens into a simple bundle and selling that bundle would transfer the control of all of the tokens to the buyer in a single transaction.
Collecting
A lot of NFT consumers collect them based on countless criteria. Some aim for utility of the tokens, some for the uniqueness, some for the visual appeal, etc. There is no standardized way to group the NFTs tied to a specific account. By nesting NFTs based on their owner’s preference, this proposal introduces the ability to do it. The root parent token could represent a certain group of tokens and all of the children nested into it would belong to it.
The rise of soulbound, non-transferable, tokens, introduces another need for this proposal. Having a token with multiple soulbound traits (child tokens), allows for numerous use cases. One concrete example of this can be drawn from supply trains use case. A shipping container, represented by an NFT with its own traits, could have multiple child tokens denoting each leg of its journey.
Membership
A common utility attached to NFTs is a membership to a Decentralised Autonomous Organization (DAO) or to some other closed-access group. Some of these organizations and groups occasionally mint NFTs to the current holders of the membership NFTs. With the ability to nest mint a token into a token, such minting could be simplified, by simply minting the bonus NFT directly into the membership one.
Delegation
One of the core features of DAOs is voting and there are various approaches to it. One such mechanic is using fungible voting tokens where members can delegate their votes by sending these tokens to another member. Using this proposal, delegated voting could be handled by nesting your voting NFT into the one you are delegating your votes to and transferring it when the member no longer wishes to delegate their votes.
规范
The key words “MUST”, “MUST NOT”, “REQUIRED”, “SHALL”, “SHALL NOT”, “SHOULD”, “SHOULD NOT”, “RECOMMENDED”, “MAY”, and “OPTIONAL” in this document are to be interpreted as described in RFC 2119.
/// @title EIP-6059 Parent-Governed Nestable Non-Fungible Tokens
/// @dev See https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-6059
/// @dev Note: the ERC-165 identifier for this interface is 0x60b766e5.
pragma solidity ^0.8.16;
interface INestable {
/**
* @notice The core struct of ownership.
* @dev The `DirectOwner` struct is used to store information of the next immediate owner, be it the parent token,
* an `ERC721Receiver` contract or an externally owned account.
* @dev If the token is not owned by an NFT, the `tokenId` MUST equal `0`.
* @param tokenId ID of the parent token
* @param ownerAddress Address of the owner of the token. If the owner is another token, then the address MUST be
* the one of the parent token's collection smart contract. If the owner is externally owned account, the address
* MUST be the address of this account
* @param isNft A boolean value signifying whether the token is owned by another token (`true`) or by an externally
* owned account (`false`)
*/
struct DirectOwner {
uint256 tokenId;
address ownerAddress;
bool isNft;
}
/**
* @notice Used to notify listeners that the token is being transferred.
* @dev Emitted when `tokenId` token is transferred from `from` to `to`.
* @param from Address of the previous immediate owner, which is a smart contract if the token was nested.
* @param to Address of the new immediate owner, which is a smart contract if the token is being nested.
* @param fromTokenId ID of the previous parent token. If the token was not nested before, the value MUST be `0`
* @param toTokenId ID of the new parent token. If the token is not being nested, the value MUST be `0`
* @param tokenId ID of the token being transferred
*/
event NestTransfer(
address indexed from,
address indexed to,
uint256 fromTokenId,
uint256 toTokenId,
uint256 indexed tokenId
);
/**
* @notice Used to notify listeners that a new token has been added to a given token's pending children array.
* @dev Emitted when a child NFT is added to a token's pending array.
* @param tokenId ID of the token that received a new pending child token
* @param childIndex Index of the proposed child token in the parent token's pending children array
* @param childAddress Address of the proposed child token's collection smart contract
* @param childId ID of the child token in the child token's collection smart contract
*/
event ChildProposed(
uint256 indexed tokenId,
uint256 childIndex,
address indexed childAddress,
uint256 indexed childId
);
/**
* @notice Used to notify listeners that a new child token was accepted by the parent token.
* @dev Emitted when a parent token accepts a token from its pending array, migrating it to the active array.
* @param tokenId ID of the token that accepted a new child token
* @param childIndex Index of the newly accepted child token in the parent token's active children array
* @param childAddress Address of the child token's collection smart contract
* @param childId ID of the child token in the child token's collection smart contract
*/
event ChildAccepted(
uint256 indexed tokenId,
uint256 childIndex,
address indexed childAddress,
uint256 indexed childId
);
/**
* @notice Used to notify listeners that all pending child tokens of a given token have been rejected.
* @dev Emitted when a token removes all a child tokens from its pending array.
* @param tokenId ID of the token that rejected all of the pending children
*/
event AllChildrenRejected(uint256 indexed tokenId);
/**
* @notice Used to notify listeners a child token has been transferred from parent token.
* @dev Emitted when a token transfers a child from itself, transferring ownership.
* @param tokenId ID of the token that transferred a child token
* @param childIndex Index of a child in the array from which it is being transferred
* @param childAddress Address of the child token's collection smart contract
* @param childId ID of the child token in the child token's collection smart contract
* @param fromPending A boolean value signifying whether the token was in the pending child tokens array (`true`) or
* in the active child tokens array (`false`)
*/
event ChildTransferred(
uint256 indexed tokenId,
uint256 childIndex,
address indexed childAddress,
uint256 indexed childId,
bool fromPending
);
/**
* @notice The core child token struct, holding the information about the child tokens.
* @return tokenId ID of the child token in the child token's collection smart contract
* @return contractAddress Address of the child token's smart contract
*/
struct Child {
uint256 tokenId;
address contractAddress;
}
/**
* @notice Used to retrieve the *root* owner of a given token.
* @dev The *root* owner of the token is the top-level owner in the hierarchy which is not an NFT.
* @dev If the token is owned by another NFT, it MUST recursively look up the parent's root owner.
* @param tokenId ID of the token for which the *root* owner has been retrieved
* @return owner The *root* owner of the token
*/
function ownerOf(uint256 tokenId) external view returns (address owner);
/**
* @notice Used to retrieve the immediate owner of the given token.
* @dev If the immediate owner is another token, the address returned, MUST be the one of the parent token's
* collection smart contract.
* @param tokenId ID of the token for which the direct owner is being retrieved
* @return address Address of the given token's owner
* @return uint256 The ID of the parent token. MUST be `0` if the owner is not an NFT
* @return bool The boolean value signifying whether the owner is an NFT or not
*/
function directOwnerOf(uint256 tokenId)
external
view
returns (
address,
uint256,
bool
);
/**
* @notice Used to burn a given token.
* @dev When a token is burned, all of its child tokens are recursively burned as well.
* @dev When specifying the maximum recursive burns, the execution MUST be reverted if there are more children to be
* burned.
* @dev Setting the `maxRecursiveBurn` value to 0 SHOULD only attempt to burn the specified token and MUST revert if
* there are any child tokens present.
* @param tokenId ID of the token to burn
* @param maxRecursiveBurns Maximum number of tokens to recursively burn
* @return uint256 Number of recursively burned children
*/
function burn(uint256 tokenId, uint256 maxRecursiveBurns)
external
returns (uint256);
/**
* @notice Used to add a child token to a given parent token.
* @dev This adds the child token into the given parent token's pending child tokens array.
* @dev The destination token MUST NOT be a child token of the token being transferred or one of its downstream
* child tokens.
* @dev This method MUST NOT be called directly. It MUST only be called from an instance of `INestable` as part of a
`nestMint`, `nestTransfer` or `transferChild` to an NFT.
* @dev Requirements:
*
* - `directOwnerOf` on the child contract MUST resolve to the called contract.
* - the pending array of the parent contract MUST not be full.
* @param parentId ID of the parent token to receive the new child token
* @param childId ID of the new proposed child token
*/
function addChild(uint256 parentId, uint256 childId) external;
/**
* @notice Used to accept a pending child token for a given parent token.
* @dev This moves the child token from parent token's pending child tokens array into the active child tokens
* array.
* @param parentId ID of the parent token for which the child token is being accepted
* @param childIndex Index of the child token to accept in the pending children array of a given token
* @param childAddress Address of the collection smart contract of the child token expected to be at the specified
* index
* @param childId ID of the child token expected to be located at the specified index
*/
function acceptChild(
uint256 parentId,
uint256 childIndex,
address childAddress,
uint256 childId
) external;
/**
* @notice Used to reject all pending children of a given parent token.
* @dev Removes the children from the pending array mapping.
* @dev The children's ownership structures are not updated.
* @dev Requirements:
*
* - `parentId` MUST exist
* @param parentId ID of the parent token for which to reject all of the pending tokens
* @param maxRejections Maximum number of expected children to reject, used to prevent from
* rejecting children which arrive just before this operation.
*/
function rejectAllChildren(uint256 parentId, uint256 maxRejections) external;
/**
* @notice Used to transfer a child token from a given parent token.
* @dev MUST remove the child from the parent's active or pending children.
* @dev When transferring a child token, the owner of the token MUST be set to `to`, or not updated in the event of `to`
* being the `0x0` address.
* @param tokenId ID of the parent token from which the child token is being transferred
* @param to Address to which to transfer the token to
* @param destinationId ID of the token to receive this child token (MUST be 0 if the destination is not a token)
* @param childIndex Index of a token we are transferring, in the array it belongs to (can be either active array or
* pending array)
* @param childAddress Address of the child token's collection smart contract
* @param childId ID of the child token in its own collection smart contract
* @param isPending A boolean value indicating whether the child token being transferred is in the pending array of the
* parent token (`true`) or in the active array (`false`)
* @param data Additional data with no specified format, sent in call to `to`
*/
function transferChild(
uint256 tokenId,
address to,
uint256 destinationId,
uint256 childIndex,
address childAddress,
uint256 childId,
bool isPending,
bytes data
) external;
/**
* @notice Used to retrieve the active child tokens of a given parent token.
* @dev Returns array of Child structs existing for parent token.
* @dev The Child struct consists of the following values:
* [
* tokenId,
* contractAddress
* ]
* @param parentId ID of the parent token for which to retrieve the active child tokens
* @return struct[] An array of Child structs containing the parent token's active child tokens
*/
function childrenOf(uint256 parentId)
external
view
returns (Child[] memory);
/**
* @notice Used to retrieve the pending child tokens of a given parent token.
* @dev Returns array of pending Child structs existing for given parent.
* @dev The Child struct consists of the following values:
* [
* tokenId,
* contractAddress
* ]
* @param parentId ID of the parent token for which to retrieve the pending child tokens
* @return struct[] An array of Child structs containing the parent token's pending child tokens
*/
function pendingChildrenOf(uint256 parentId)
external
view
returns (Child[] memory);
/**
* @notice Used to retrieve a specific active child token for a given parent token.
* @dev Returns a single Child struct locating at `index` of parent token's active child tokens array.
* @dev The Child struct consists of the following values:
* [
* tokenId,
* contractAddress
* ]
* @param parentId ID of the parent token for which the child is being retrieved
* @param index Index of the child token in the parent token's active child tokens array
* @return struct A Child struct containing data about the specified child
*/
function childOf(uint256 parentId, uint256 index)
external
view
returns (Child memory);
/**
* @notice Used to retrieve a specific pending child token from a given parent token.
* @dev Returns a single Child struct locating at `index` of parent token's active child tokens array.
* @dev The Child struct consists of the following values:
* [
* tokenId,
* contractAddress
* ]
* @param parentId ID of the parent token for which the pending child token is being retrieved
* @param index Index of the child token in the parent token's pending child tokens array
* @return struct A Child struct containing data about the specified child
*/
function pendingChildOf(uint256 parentId, uint256 index)
external
view
returns (Child memory);
/**
* @notice Used to transfer the token into another token.
* @dev The destination token MUST NOT be a child token of the token being transferred or one of its downstream
* child tokens.
* @param from Address of the direct owner of the token to be transferred
* @param to Address of the receiving token's collection smart contract
* @param tokenId ID of the token being transferred
* @param destinationId ID of the token to receive the token being transferred
*/
function nestTransferFrom(
address from,
address to,
uint256 tokenId,
uint256 destinationId
) external;
}
ID MUST never be a 0 value, as this proposal uses 0 values do signify that the token/destination is not an NFT.
基本原理
Designing the proposal, we considered the following questions:
- How to name the proposal?
In an effort to provide as much information about the proposal we identified the most important aspect of the proposal; the parent centered control over nesting. The child token’s role is only to be able to be Nestable and support a token owning it. This is how we landed on the Parent-Centered part of the title.
- Why is automatically accepting a child using EIP-712 permit-style signatures not a part of this proposal?
For consistency. This proposal extends EIP-721 which already uses 1 transaction for approving operations with tokens. It would be inconsistent to have this and also support signing messages for operations with assets.
- Why use indexes?
To reduce the gas consumption. If the token ID was used to find which token to accept or reject, iteration over arrays would be required and the cost of the operation would depend on the size of the active or pending children arrays. With the index, the cost is fixed. Lists of active and pending children per token need to be maintained, since methods to get them are part of the proposed interface.
To avoid race conditions in which the index of a token changes, the expected token ID as well as the expected token’s collection smart contract is included in operations requiring token index, to verify that the token being accessed using the index is the expected one.
Implementation that would internally keep track of indices using mapping was attempted. The minimum cost of accepting a child token was increased by over 20% and the cost of minting has increased by over 15%. We concluded that it is not necessary for this proposal and can be implemented as an extension for use cases willing to accept the increased transaction cost this incurs. In the sample implementation provided, there are several hooks which make this possible.
- Why is the pending children array limited instead of supporting pagination?
The pending child tokens array is not meant to be a buffer to collect the tokens that the root owner of the parent token wants to keep, but not enough to promote them to active children. It is meant to be an easily traversable list of child token candidates and should be regularly maintained; by either accepting or rejecting proposed child tokens. There is also no need for the pending child tokens array to be unbounded, because active child tokens array is.
Another benefit of having bounded child tokens array is to guard against spam and griefing. As minting malicious or spam tokens could be relatively easy and low-cost, the bounded pending array assures that all of the tokens in it are easy to identify and that legitimate tokens are not lost in a flood of spam tokens, if one occurs.
A consideration tied to this issue was also how to make sure, that a legitimate token is not accidentally rejected when clearing the pending child tokens array. We added the maximum pending children to reject argument to the clear pending child tokens array call. This assures that only the intended number of pending child tokens is rejected and if a new token is added to the pending child tokens array during the course of preparing such call and executing it, the clearing of this array SHOULD result in a reverted transaction.
- Should we allow tokens to be nested into one of its children?
The proposal enforces that a parent token can’t be nested into one of its child token, or downstream child tokens for that matter. A parent token and its children are all managed by the parent token’s root owner. This means that if a token would be nested into one of its children, this would create the ownership loop and none of the tokens within the loop could be managed anymore.
- Why is there not a “safe” nest transfer method?
nestTransfer is always “safe” since it MUST check for INestable compatibility on the destination.
- How does this proposal differ from the other proposals trying to address a similar problem?
This interface allows for tokens to both be sent to and receive other tokens. The propose-accept and parent governed patterns allow for a more secure use. The backward compatibility is only added for EIP-721, allowing for a simpler interface. The proposal also allows for different collections to inter-operate, meaning that nesting is not locked to a single smart contract, but can be executed between completely separate NFT collections.
Propose-Commit pattern for child token management
Adding child tokens to a parent token MUST be done in the form of propose-commit pattern to allow for limited mutability by a 3rd party. When adding a child token to a parent token, it is first placed in a “Pending” array, and MUST be migrated to the “Active” array by the parent token’s root owner. The “Pending” child tokens array SHOULD be limited to 128 slots to prevent spam and griefing.
The limitation that only the root owner can accept the child tokens also introduces a trust inherent to the proposal. This ensures that the root owner of the token has full control over the token. No one can force the user to accept a child if they don’t want to.
Parent Governed pattern
The parent NFT of a nested token and the parent’s root owner are in all aspects the true owners of it. Once you send a token to another one you give up ownership.
We continue to use EIP-721’s ownerOf functionality which will now recursively look up through parents until it finds an address which is not an NFT, this is referred to as the root owner. Additionally we provide the directOwnerOf which returns the most immediate owner of a token using 3 values: the owner address, the tokenId which MUST be 0 if the direct owner is not an NFT, and a flag indicating whether or not the parent is an NFT.
The root owner or an approved party MUST be able do the following operations on children: acceptChild, rejectAllChildren and transferChild.
The root owner or an approved party MUST also be allowed to do these operations only when token is not owned by an NFT: transferFrom, safeTransferFrom, nestTransferFrom, burn.
If the token is owned by an NFT, only the parent NFT itself MUST be allowed to execute the operations listed above. Transfers MUST be done from the parent token, using transferChild, this method in turn SHOULD call nestTransferFrom or safeTransferFrom in the child token’s smart contract, according to whether the destination is an NFT or not. For burning, tokens must first be transferred to an EOA and then burned.
We add this restriction to prevent inconsistencies on parent contracts, since only the transferChild method takes care of removing the child from the parent when it is being transferred out of it.
Child token management
This proposal introduces a number of child token management functions. In addition to the permissioned migration from “Pending” to “Active” child tokens array, the main token management function from this proposal is the tranferChild function. The following state transitions of a child token are available with it:
- Reject child token
- Abandon child token
- Unnest child token
- Transfer the child token to an EOA or an
ERC721Receiver - Transfer the child token into a new parent token
To better understand how these state transitions are achieved, we have to look at the available parameters passed to transferChild:
function transferChild(
uint256 tokenId,
address to,
uint256 destinationId,
uint256 childIndex,
address childAddress,
uint256 childId,
bool isPending,
bytes data
) external;
Based on the desired state transitions, the values of these parameters have to be set accordingly (any parameters not set in the following examples depend on the child token being managed):
- Reject child token
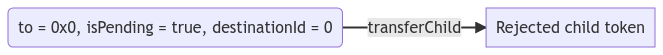
- Abandon child token
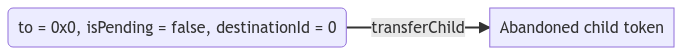
- Unnest child token

- Transfer the child token to an EOA or an
ERC721Receiver

- Transfer the child token into a new parent token

This state change places the token in the pending array of the new parent token. The child token still needs to be accepted by the new parent token’s root owner in order to be placed into the active array of that token.
向后兼容性
The Nestable token standard has been made compatible with EIP-721 in order to take advantage of the robust tooling available for implementations of EIP-721 and to ensure compatibility with existing EIP-721 infrastructure.
测试用例
Tests are included in nestable.ts.
To run them in terminal, you can use the following commands:
cd ../assets/eip-6059
npm install
npx hardhat test
Reference Implementation
See NestableToken.sol.
Security Considerations
The same security considerations as with EIP-721 apply: hidden logic may be present in any of the functions, including burn, add resource, accept resource, and more.
Caution is advised when dealing with non-audited contracts.
版权声明
Copyright and related rights waived via CC0.
参考文献
Please cite this document as:
Bruno Škvorc, Cicada, Steven Pineda, Stevan Bogosavljevic, Jan Turk, "EIP-6059: Parent-Governed Nestable Non-Fungible Tokens [DRAFT]," Ethereum Improvement Proposals, no. 6059, November 2022. [Online serial]. Available: https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-6059.